Solid-state e-bike battery technology | Electric bike review

Some links may be affiliate links. We may be paid if you purchase something or take an action after clicking one of these options.
This expensive but cutting-edge e-bike technology is the “holy grail” of rechargeable power sources.


Enormous range, lightning-fast charging and more safety – this could be the future of e-bike batteries!
Swiss fast pedelec (or S-Pedelec) brand Stromer is a leader in the development of electric bike batteries and has teamed up with TD Hitech Energy to produce a ceramic solid-state battery with the above goals. Not even that best electric bikes The devices currently available on the market can live up to this potential!
Stromer presented its first drivable prototype at the world championship Eurobike E-Mobility Congress Earlier this year in Frankfurt, Germany, the foundation was laid for other e-bike brands to follow.
While the technology is still in development — and likely won’t be available to consumers for at least two to three years — Stromer and his partner are aiming high. The developers’ goal is to develop safer, longer-lasting batteries with shorter charging times and low-temperature charging capability.
The shortcomings of lithium-ion e-bike batteries
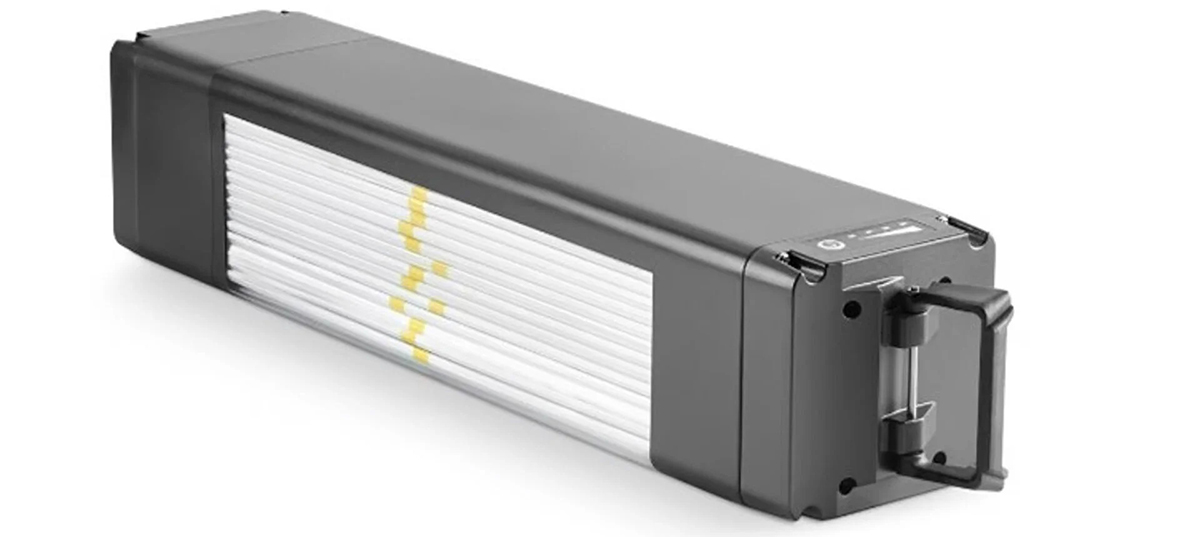
Lithium-ion batteries, currently the ubiquitous gold standard for e-bikes, use a liquid or gel electrolyte to transport charged ions between two internal terminals within each cell. The reactions caused by this process effectively store and discharge energy from batteries, but this aging technology has its drawbacks.
“Dendrites,” or branched deposits, of lithium can build up in these battery cells and cause short circuits, while the conductive liquid electrolyte solution used to transport the ions does known to be highly flammable. Lithium-ion technology has proven to be the most reliable and cost-effective solution for mass production, but its shortcomings are increasingly drawing criticism.


Lithium-ion batteries are large and heavy; A solid-state battery of the same size and weight could carry twice as much energy and therefore achieve twice the range.
The advantages of solid-state batteries for e-bikes
Solid-state batteries, on the other hand, use a solid electrolyte to transfer ions, and in the case of Stromer’s battery, this material is (at least partially) made of ceramic. This technology is currently associated with significant costs, but promises numerous advantages over lithium-ion power sources.
With little or no liquid electrolyte solution – and therefore less leakage and corrosion – solid-state batteries have the potential for a much longer lifespan. Research from Harvard University suggests that solid-state batteries could have as much as 50% 10,000 charging cycles, which means they last between 10 and 15 years. They are also less likely to catch fire due to their improved thermal and electrochemical stability.
Of course, due to the composition of their solid electrolyte, solid-state batteries also have a higher energy density than current lithium-ion batteries, meaning a similarly sized solid-state battery pack could store twice the energy and provide twice the range of an e-bike. Finally, the technology could also be more sustainable due to the reduced need for rare metals such as cobalt and graphite.
The challenges of solid-state e-bike battery technology
Manufacturing capacity and cost are two of the biggest hurdles for solid-state technology, as explained in a MotorTrend article about EV batteries.
Currently, solid-state technology exists in tiny button cells used in small, lightweight devices like smartwatches and pacemakers. Expanding this technology to meet the needs of larger, more sophisticated machines such as e-bikes requires the development and rationalization of dedicated manufacturing processes and equipment.
Because these mass production capabilities do not yet exist, producing a solid-state battery and its unique components is difficult. Solid-state batteries may also require more lithium than lithium-ion batteries, a material that has only become more expensive and difficult to source in recent years. With these additional costs, a solid-state battery is currently eight times more expensive to produce than a lithium-ion battery.
As technology and its manufacturing processes advance, the potential benefits of solid-state batteries are becoming increasingly clear. In the case of Stromer and TD Hitech Energy, they hope to produce power sources with ten times faster charging times (currently 20 minutes with an end goal of 12 minutes) and the ability to charge in temperatures as low as -4 °F (-20 °C). a target of -22°F (-30°C).
Present and future of solid-state batteries
Taiwan appears to be a hotbed of solid state research, as both TD Hitech Energy and its competitor ProLogium are headquartered in the country’s northern cities. However, the race continues as researchers around the world – including in the US – are dedicated to the cause.
ProLogium has been working with European automakers such as Mercedes-Benz to develop solid-state batteries for use in electric vehicles and is set to begin doing so testing later this year. The developer has an established foundation, having produced prototypes of replaceable solid-state batteries in collaboration with a Taiwanese electric scooter manufacturer Gogoro in 2022.
Here in the USA, NASA has already claimed to have a solid-state battery that could power an aircraft. Researcher on Georgia Institute of Technology are working to transfer their success with solid-state button cell technology to pouch cells for use in electric vehicles.
No matter how you look at it, solid-state technology is clearly on the rise. The market was valued at almost $591 million in 2020and its expansion was forecast to exhibit a consistent compound annual growth rate of 36% from 2021 to 2028.
Here, at Electric bike review, we look forward to the leaps this new technology could soon bring. We plan to keep an eye on the development of this potentially industry-changing technology and will continue to share any new and exciting updates as they appear.
Sponsors
Reader interactions
![]()
![]()